Enterprise Architectural Evaluation of Agentic Patterns
When selecting and implementing agentic design patterns, enterprises must evaluate them against critical architectural dimensions to ensure they meet business requirements and operational standards. This evaluation framework provides a comprehensive approach to assessing patterns across key enterprise concerns.
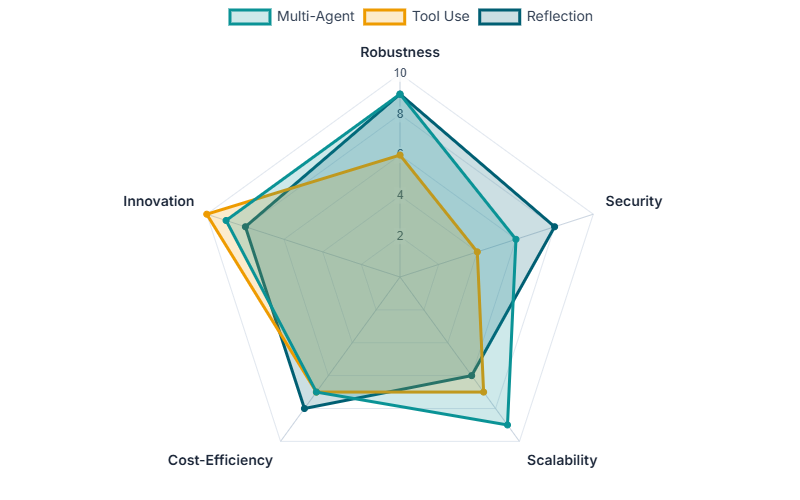
Impact Matrix
| Pattern | Robustness | Security | Scalability | Cost-Efficiency | Innovation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | High | Medium | High | Medium | Medium |
| Tool Use | Medium | Low | Medium | High | High |
| Reflection | High | High | Medium | Medium | High |
| Multi-Agent | High | Low | High | Medium | High |
| ReAct | Medium | Medium | High | High | Medium |
| Plan-and-Execute | High | High | Medium | Medium | Medium |
Robustness and Reliability
Evaluation
Assess error handling capabilities, graceful degradation, and resilience to unexpected inputs or tool failures. Patterns like Reflection are crucial for self-healing and maintaining reliability.
Impact
Ensures mission-critical applications remain stable and perform consistently, minimizing downtime and data corruption.
Pattern-Specific Assessment
- Planning Pattern: Enhances system robustness by enabling the decomposition of complex tasks into manageable, often independent, sub-tasks. This modularity allows for better error isolation and facilitates graceful degradation in case of partial failures.
- Tool Use Pattern: Increases system robustness by leveraging external, specialized, and often highly robust enterprise systems (such as databases, APIs, or legacy applications). However, it inherently introduces dependencies on the reliability and availability of these external systems.
- Reflection Pattern: Significantly improves the quality and reliability of agent outputs by identifying and correcting errors, biases, or inconsistencies. It acts as an internal quality gate, enhancing the system's overall dependability.
- Multi-Agent Pattern: The distributed architecture inherent in the Multi-Agent Pattern offers built-in redundancy and fail-safe mechanisms. Failures in one agent can often be isolated, preventing cascading system-wide failures and enhancing overall system resilience.
- ReAct Pattern: Its iterative nature allows for dynamic adjustment and potential recovery from intermediate errors or unexpected observations, enhancing resilience for simpler, well-defined tasks.
- Plan-and-Execute Pattern: The explicit planning and execution phases, coupled with opportunities for intermediate result validation, allow for better error detection and dynamic plan adjustment, making it highly robust for complex and critical tasks.
Scalability and Performance
Evaluation
Consider the ability of patterns to handle increasing workloads and process requests efficiently. Parallelization is key for throughput, while efficient Prompt Chaining and Routing can optimize resource usage.
Impact
Supports growth in user demand and data volume without compromising response times or incurring prohibitive costs.
Pattern-Specific Assessment
- Planning Pattern: Directly facilitates parallel execution of sub-tasks, significantly improving overall system throughput and responsiveness for complex operations.
- Tool Use Pattern: The scalability of an agentic system heavily depends on the scalability of the integrated tools and external APIs. If external systems are not designed for high concurrency or throughput, they can become a significant bottleneck.
- Reflection Pattern: Can introduce computational overhead, especially if multiple critique LLMs or extensive validation processes are involved. Requires efficient implementation and potentially asynchronous processing to manage this overhead.
- Multi-Agent Pattern: Highly scalable due to its ability to distribute workload across multiple specialized agents. This allows for independent scaling of agent groups based on demand, optimizing resource allocation.
- ReAct Pattern: Its faster response times for simple, direct tasks make it highly scalable for high-volume, low-complexity interactions, such as those found in customer service chatbots.
- Plan-and-Execute Pattern: Moderate scalability due to the sequential nature of planning and execution phases, though it can be optimized through parallel execution of independent plan steps.
Security and Data Governance
Evaluation
Examine how patterns manage sensitive data, control access to tools and APIs, and adhere to compliance regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA). Tool Use patterns require careful access management.
Impact
Protects proprietary information, prevents unauthorized access, and maintains regulatory compliance, mitigating legal and reputational risks.
Pattern-Specific Assessment
- Planning Pattern: The planning phase can proactively identify sensitive steps or specific data access requirements, which then informs the implementation of granular access control policies for subsequent execution phases.
- Tool Use Pattern: This is a critical area. Implementing the Tool Use Pattern necessitates stringent API security measures, granular access control for agents to specific tools, robust input/output validation to prevent injection attacks, and secure management of credentials used by agents to access external systems.
- Reflection Pattern: Can be strategically used for compliance checks, identifying potential sensitive data leakage, or ensuring adherence to ethical AI guidelines within agent responses, thus bolstering the system's security posture.
- Multi-Agent Pattern: This pattern introduces complexity in security. It requires secure inter-agent communication protocols, granular access control for each agent's specific tools and data, and robust authentication mechanisms within the agent network to prevent unauthorized interactions.
- ReAct Pattern: The simpler, more direct flow of ReAct might present a smaller attack surface for complex prompt injection compared to multi-step planning patterns. However, prompt injection remains a core security risk that requires mitigation.
- Plan-and-Execute Pattern: The planning phase can incorporate explicit security checkpoints or reviews before execution, potentially enhancing control and oversight over sensitive operations.
Integration and Interoperability
Evaluation
Test API compatibility, assess data exchange, evaluate system connectivity, and monitor integration points.
Impact
Enables system collaboration, facilitates data flow, reduces integration costs, and improves operational efficiency.
Pattern-Specific Assessment
- Planning Pattern: Helps coordinate integration workflows by breaking down complex integration tasks into manageable steps and identifying dependencies between different systems.
- Tool Use Pattern: Essential for system integration as it provides the fundamental mechanism for agents to interact with external systems, APIs, and services.
- Reflection Pattern: Can validate integration results and ensure data consistency across different systems, helping to maintain integration quality and reliability.
- Multi-Agent Pattern: Enables distributed system integration by allowing different agents to specialize in interacting with specific systems while coordinating their efforts.
- ReAct Pattern: Provides a straightforward approach to system integration for simple, well-defined integration tasks, with quick feedback loops for error handling.
- Plan-and-Execute Pattern: Offers structured integration capabilities by allowing detailed planning of integration steps followed by controlled execution, suitable for complex integration scenarios.
Cost-Efficiency
Evaluation
Analyze the computational costs associated with pattern execution, particularly LLM token usage for Prompt Chaining, Reflection, and extensive Planning.
Impact
Optimizes operational expenditures, ensuring the economic viability of agentic solutions.
Pattern-Specific Assessment
- Planning Pattern: Optimized plans can reduce redundant steps and minimize unnecessary tool calls or computations, leading to tangible cost savings in resource consumption.
- Tool Use Pattern: Leverages existing enterprise investments in tools and systems, avoiding the need for re-implementation of functionality. However, operational costs are directly tied to external API usage fees and potentially the infrastructure required for tool management.
- Reflection Pattern: Reduces the need for manual review and correction, prevents costly errors in critical outputs, and generally improves the accuracy and trustworthiness of the system, leading to long-term cost savings.
- Multi-Agent Pattern: Optimizes resource utilization through specialization, as agents can be highly efficient within their specific domains. However, the initial setup and orchestration complexity can incur higher development and management costs.
- ReAct Pattern: Lower token usage and fewer API calls per task contribute to its higher cost-efficiency for frequent, straightforward operations.
- Plan-and-Execute Pattern: Generally incurs a higher cost per task due to increased token usage and more API calls, making it less suitable for highly cost-sensitive, simple tasks.
Continuous Innovation
Evaluation
Assess how easily patterns can be updated, extended, or integrated with new technologies. Modularity provided by Routing and Multi-Agent patterns can foster adaptability.
Impact
Enables rapid iteration, integration of new AI models or tools, and responsiveness to evolving business needs and technological advancements.
Pattern-Specific Assessment
- Planning Pattern: Supports dynamic adaptation and re-planning capabilities, allowing the system to respond effectively to changing requirements or unforeseen circumstances, thereby fostering continuous agility and evolution.
- Tool Use Pattern: Unlocks vast potential by enabling agents to interact with real-world data and execute actions directly within enterprise systems. This capability creates entirely new avenues for automation, intelligent decision support, and novel business processes.
- Reflection Pattern: Drives continuous improvement and self-optimization of agent behavior. This allows systems to learn and adapt over time without requiring explicit re-training cycles, fostering ongoing innovation and adaptability.
- Multi-Agent Pattern: Fosters emergent behaviors and enables the solution of highly complex, multi-faceted problems by mimicking human team collaboration, leading to innovative approaches to business challenges.
- ReAct Pattern: Enables dynamic, real-time interaction and quick problem-solving for well-defined tasks, supporting agile and responsive applications.
- Plan-and-Execute Pattern: Enables tackling highly complex, multi-faceted problems that require structured reasoning and precise execution, unlocking new levels of automation and intelligence for intricate business processes.